1
/
of
1
PANEN77
PANEN77 | Link Login Apk Paling Viral Hari ini
PANEN77 | Link Login Apk Paling Viral Hari ini
Regular price
KHR10,000.00
Regular price
Sale price
KHR10,000.00
Unit price
/
per
Couldn't load pickup availability
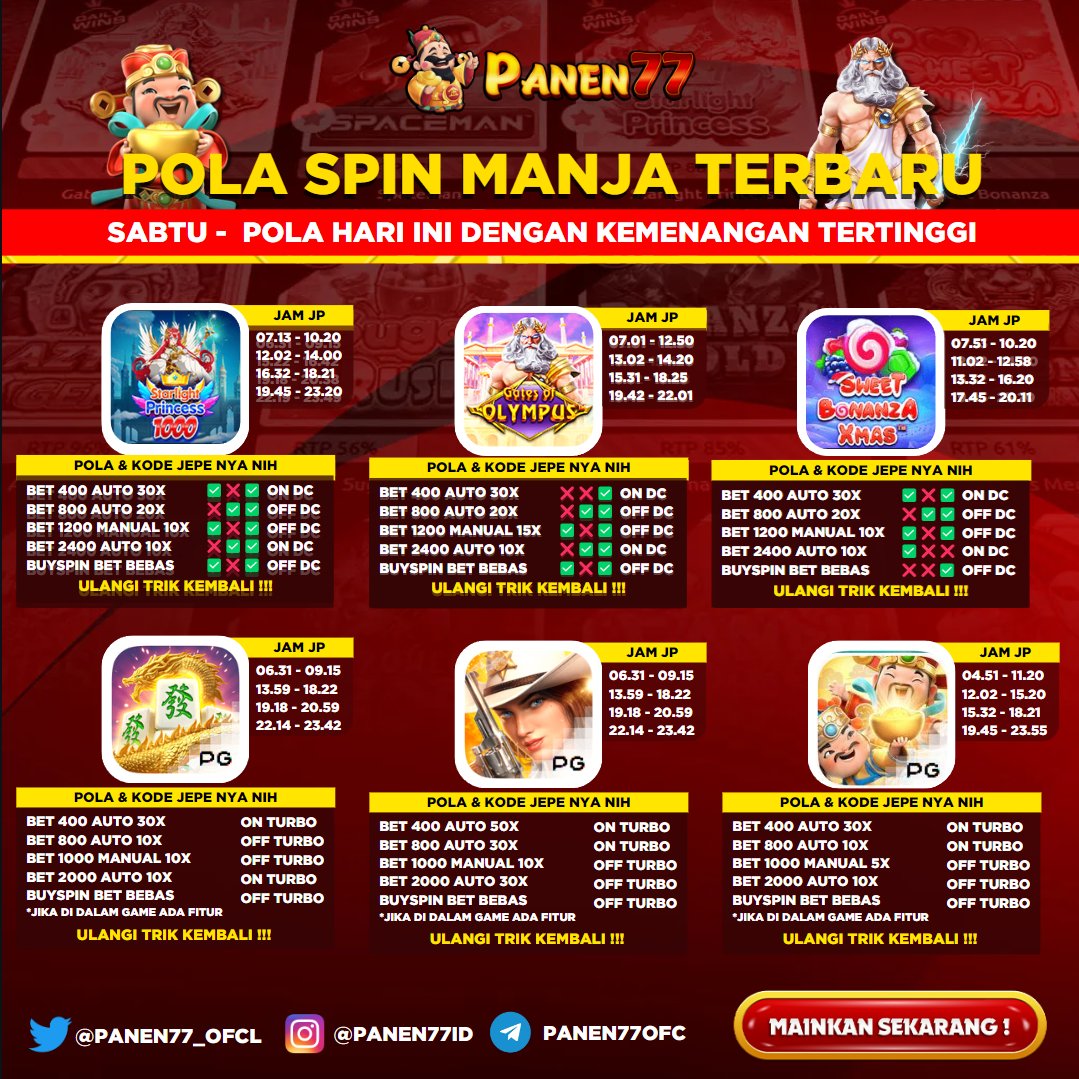
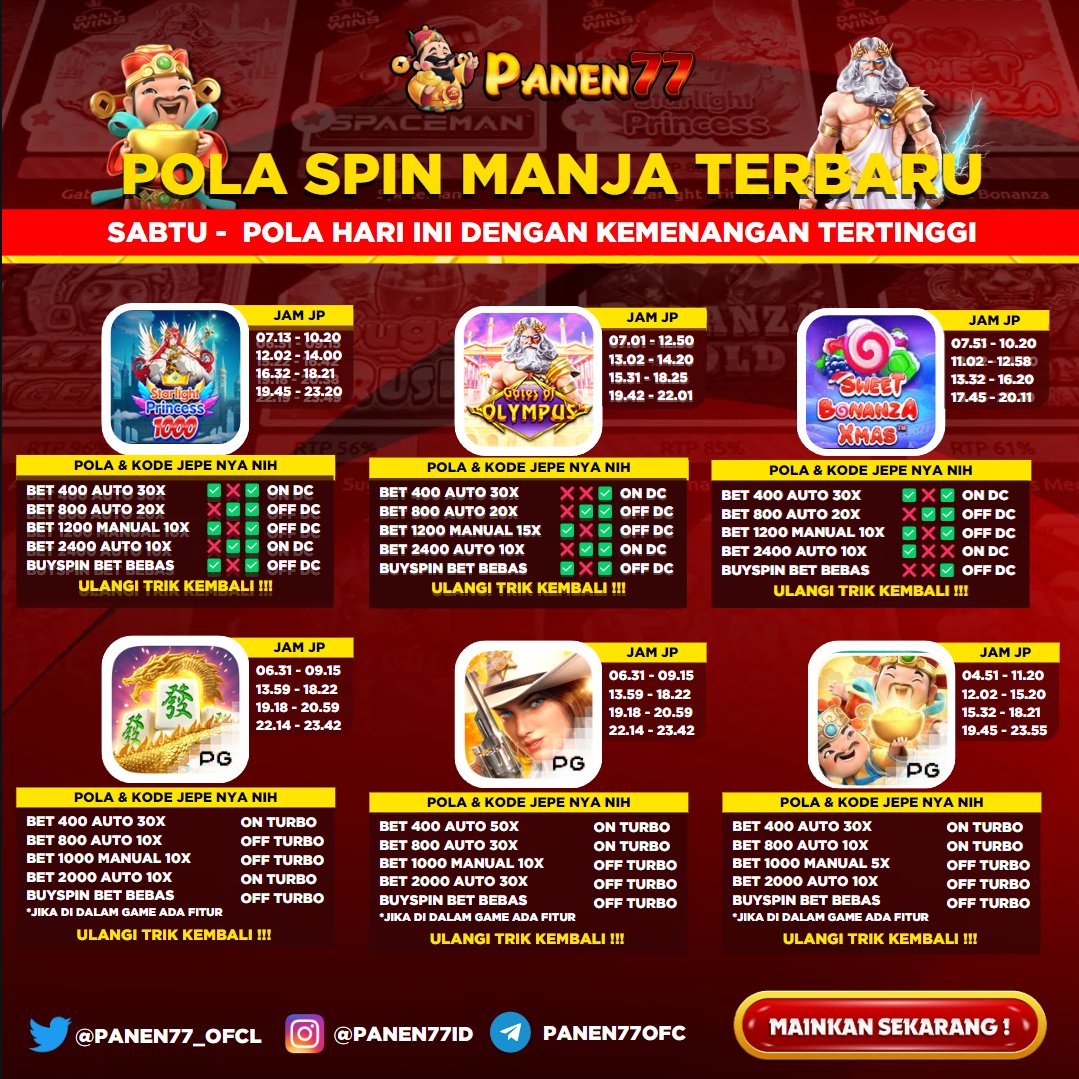
Panen77 merupkan penyedia permainan yang sangat populer dikalangan masyarakat, dengan akses yang mudah dan dapat dimainkan melalui smartphone kalian dapat memaikan game di situs panen77 dengan dimanapun dengan terhubung internet. Game online ini memberikan sensasi dan pengalman baru saat dimainkan. Panen 77 menyediakan lebih dari 777 game. Kalian dapat memilih permainan yang menjadi favorit anda di slot online terpecaya.

Share